Home / Docs / Release 0.6.2 / Get Started / Architecture
Architecture
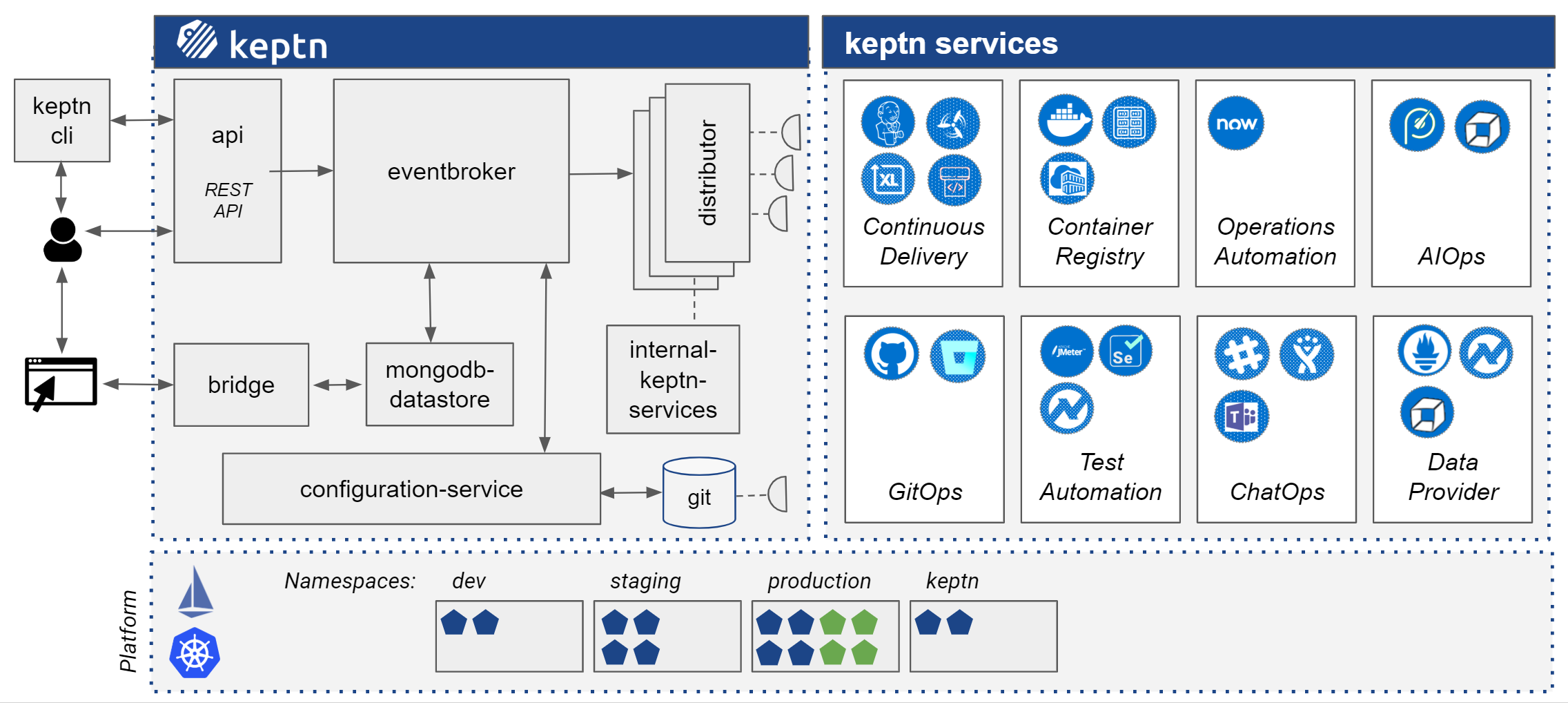
Keptn is a control plane for continuous delivery that runs on Kubernetes. When installing Keptn on a Kubernetes cluster, core components, Tiller, and Istio are installed. Keptn itself follows an event-driven approach with the benefits of loosely coupled components and a flexible design that allows easily integrating other components and services. The events that Keptn understands are specified here and follow the Cloud Events specification v2.
Prerequisites
During a Keptn installation, following components are installed on the Kubernetes cluster:
Keptn CLI
The Keptn CLI needs to be installed on the local machine and is used to send commands to Keptn. To communicate with Keptn you need to know a shared secret that is generated during the installation and verified by the api component.
Note: A dedicated Keptn CLI section is provided here, which helps you to get started and lists all commands that are currently available.
Keptn core components
Keptn has a number of core components that are set up during the installation.
api
The api component provides a publicly exposed REST API that allows to communicate with Keptn. Thus, it receives the commands from the CLI and executes the requested tasks. However, the api component mostly uses other internal services or forwards events to the eventbroker. In addition to the REST API, the api component maintains a websocket server to forward Keptn messages to the Keptn CLI.
eventbroker
The eventbroker is responsible for receiving all events, transferring non-Keptn events into valid Keptn Cloud Events, and sending those into NATS.
distributor
A distributor receives event messages from NATS and sends the events to services that have a subscription to the event topic. Thus, each service has its own distributor that is configured for the events to receive/send and the subscribed service.
mongodb-datastore
The mongodb-datastore provides means to store event and log data in a mongodb deployed in your Keptn cluster. In its current implementation, the service provides two REST endpoints: (1) /events, (2) /logs. Stored data can be requested by using those endpoints.
bridge
The Keptn Bridge lets a user browse the Keptn’s log by providing a user interface that shows all Keptn events and log messages correlated to those events.
Note: A dedicated section for the Keptn Bridge is provided here, which explains how to access it and shows the user interface.
configuration-service
The configuration-service is a Keptn core component and used to manage resources for Keptn project-related entities, i.e., project, stage, and service. The entity model is shown below. To store the resources with version control, a Git repository is used that is mounted as persistent volume. Besides, this service has functionality to upload the Git repository to any Git-based service such as GitLab, GitHub, Bitbucket, etc.
Entity model
------------ ------------ ------------
| | 1 | | 1 | |
| Project |----------| Stage |----------| Service |
| | * | | * | |
------------ ------------ ------------
1 \ 1 \ 1 \
\ * \ * \ *
------------ ------------ ------------
| | | | | |
| Resource | | Resource | | Resource |
| | | | | |
------------ ------------ ------------
internal-keptn-services
This category of services reacts on Keptn events and perform: (1) initial tasks like creating a project or creating a service, (2) continuous delivery tasks like deploying or promoting a service, and (3) continuous operations tasks such as scaling a replica set or rolling back a deployment.
shipyard-service: It is responsible for creating a project and processing a shipyard file that defines the stages each deployment has to go through until it is released to end-users.
helm-service: It has two responsibilities: (1) creates/modifies the configuration of a service that is going to be onboarded, and (2) fetches configuration files from the configuration-service and applies those using Helm. The current Helm version used by this service is helm 2.12.3.
wait-service: It is responsible for delaying a Keptn workflow for a specified duration.
gatekeeper-service: It implements the quality gate in each stage, i.e., depending on the evaluation result it either promotes an artifact to the next stage or not.
remediation-service: It uses the remediation configuration of a service and execute the tasks specified there.
Keptn services
To enrich the continuous delivery as well as the continuous operations use cases, Keptn relies on services from the community. Those services can be easily plugged into the workflows to enrich the delivery pipeline or to further automate operations.
Note: A dedicated tutorial is provided here, which helps you to implement a custom service for Keptn.