Home / Docs / Release 0.6.2 / Reference / Setup Monitoring / Prometheus
Prometheus
In order to evaluate the quality gates and allow self-healing in production, we have to set up monitoring to get the needed data.
Prerequisites
- To setup Prometheus monitoring for you Kubernetes cluster, a Keptn project and at least one onboarded service must be available. For example, finish the Onboarding a Service tutorial or onboard your own service.
Setup Prometheus
After creating a project and service, you can setup Prometheus monitoring and configure scrape jobs using the Keptn CLI.
To install the prometheus-service, execute:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keptn-contrib/prometheus-service/release-0.3.3/deploy/service.yamlExecute the following command to set up the rules for the Prometheus Alerting Manager:
keptn configure monitoring prometheus --project=PROJECTNAME --service=SERVICENAME
Verify Prometheus setup in your cluster
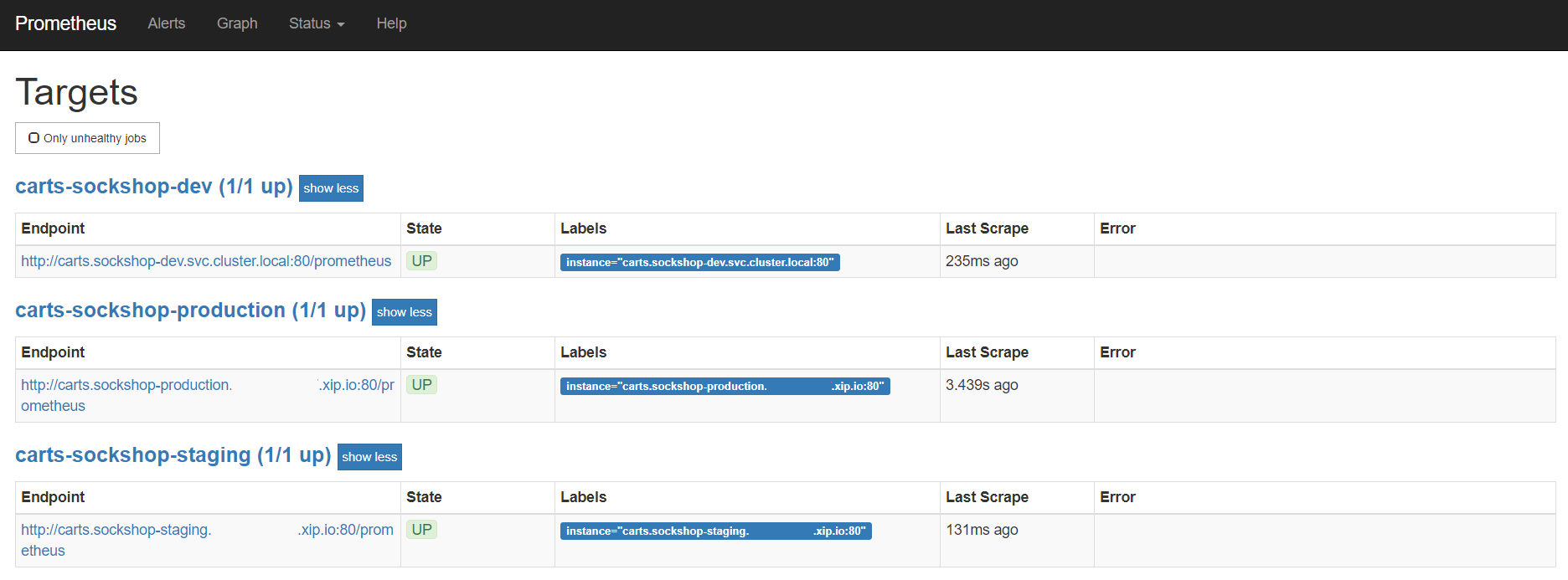
To verify that the Prometheus scrape jobs are correctly set up, you can access Prometheus by enabling port-forwarding for the prometheus-service:
kubectl port-forward svc/prometheus-service 8080 -n monitoring
Prometheus is then available on localhost:8080/targets where you can see the targets for the service:
Setup Prometheus SLI provider
During the evaluation of a quality gate, the Prometheus SLI provider is required that is implemented by an internal Keptn service, the prometheus-sli-service. This service will fetch the values for the SLIs that are referenced in a SLO configuration.
To install the prometheus-sli-service, execute:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keptn-contrib/prometheus-sli-service/0.2.2/deploy/service.yamlThe prometheus-sli-service needs access to a Prometheues instance. If you have completed the steps from Setup Prometheus, the prometheus-sli-service uses the Prometheus instance running in the cluster. Otherwise, create a secret containing the user, password, and url. The secret must have the following format (please note the double-space indentation):
user: username password: *** url: http://prometheus-service.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:8080If this information is stored in a file, e.g.
prometheus-creds.yaml, the secret can be created with the following command. Please note that there is a naming convention for the secret because this can be configured per project. Thus, the secret has to have the nameprometheus-credentials-<project>. Do not forget to replace the<project>placeholder with the name of your project:kubectl create secret -n keptn generic prometheus-credentials-<project> --from-file=prometheus-credentials=./prometheus-creds.yaml
Configure custom SLIs
To tell the prometheus-sli-service how to acquire the values of an SLI, the correct query needs to be configured. This is done by adding an SLI configuration to a project, stage, or service using the add-resource command. The resource identifier must be prometheus/sli.yaml.
Please take a look at this snippet which implements a concrete SLI file to learn more about the structure of a SLI file. It is possible to use placeholders such as $PROJECT, $SERVICE, $STAGE and $DURATION_SECONDS in the queries.
---
spec_version: '1.0'
indicators:
response_time_p50: histogram_quantile(0.5, sum by(le) (rate(http_response_time_milliseconds_bucket{job="$SERVICE-$PROJECT-$STAGE"}[$DURATION_SECONDS])))
response_time_p90: histogram_quantile(0.9, sum by(le) (rate(http_response_time_milliseconds_bucket{job="$SERVICE-$PROJECT-$STAGE"}[$DURATION_SECONDS])))
response_time_p95: histogram_quantile(0.95, sum by(le) (rate(http_response_time_milliseconds_bucket{job="$SERVICE-$PROJECT-$STAGE"}[$DURATION_SECONDS])))
- In the below example, the SLI configuration as specified in the
sli-config-prometheus.yamlfile is added to the servicecartsin stagehardeningfrom projectsockshop.
keptn add-resource --project=sockshop --stage=hardening --service=carts --resource=sli-config-prometheus.yaml --resourceUri=prometheus/sli.yaml
Note: The add-resource command can be used to store a configuration on project-, stage-, or service-level. In the context of an SLI configuration, Keptn first uses SLI configuration stored on the service-level, then on the stage-level, and finally Keptn uses SLI configuration stored on the project-level.